Project Overview
The Problem
Developers and businesses frequently need to quickly create APIs for prototypes, internal tools, or MVPs. Building custom backends is time-consuming and often overkill for simple data-driven applications. Meanwhile, valuable data sits in spreadsheets without an easy way to programmatically access it.
The Solution
SheetLayer bridges this gap by transforming Google Sheets into production-ready RESTful APIs in seconds. Users can leverage their existing spreadsheet data without writing backend code, dramatically reducing development time and technical complexity.
Key Impact
- Speed to Market: Reduced API development time from hours to minutes
- Integration: Seamless Google Sheets integration with real-time data synchronization
- Security: Magic link authentication and API key management for secure access
- Monetization: Full subscription and billing management with LemonSqueezy integration
- Performance: Redis caching for fast API responses at scale
- Developer Experience: Clean API documentation and usage analytics
Key Features
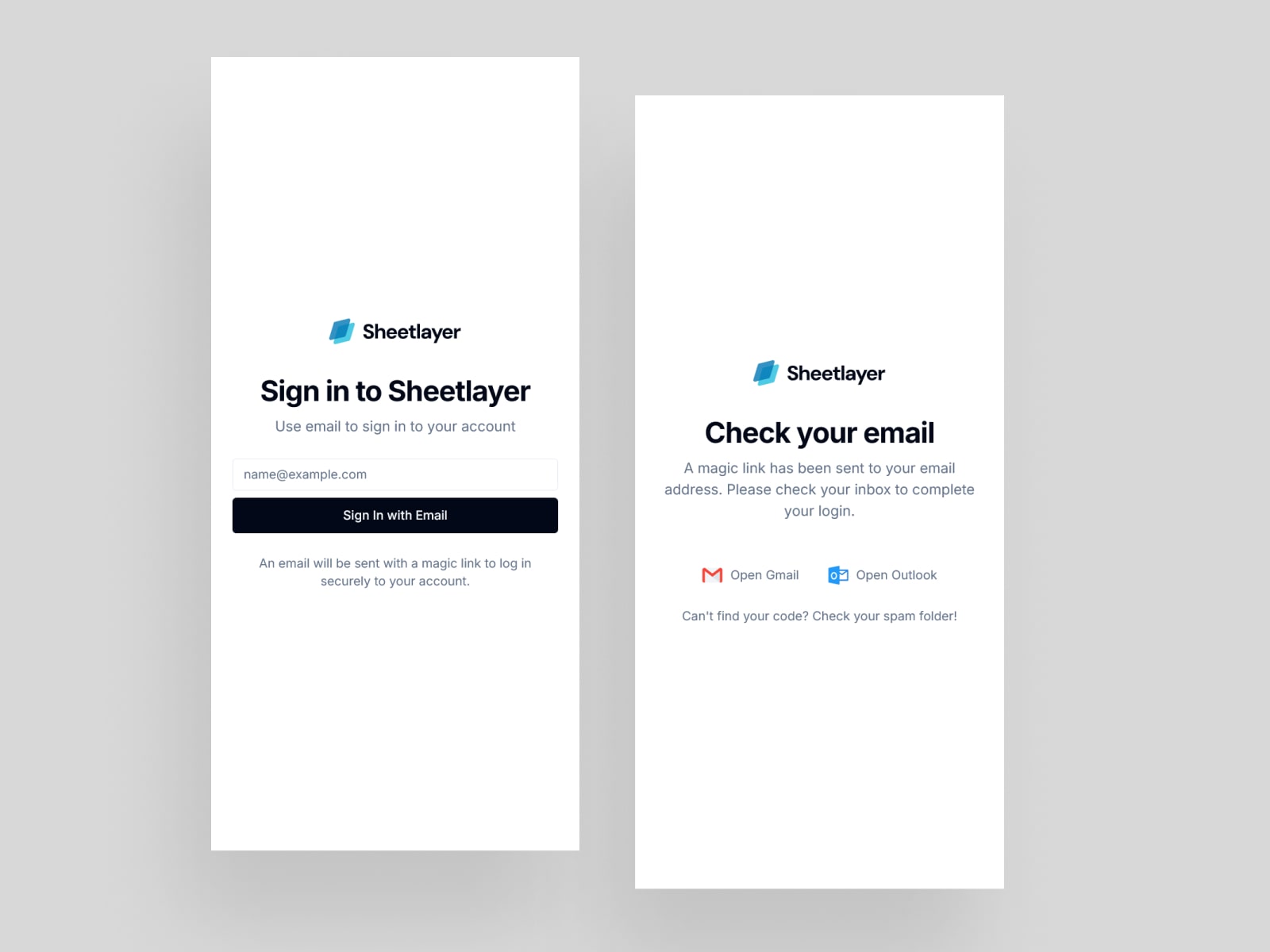
1. Secure Authentication
Simplifies user access by enabling secure, password-free login through unique, time-sensitive links sent to users' email. This feature enhances user experience and security, making it easy for teams to quickly start building APIs from their spreadsheet data.
2. Google Sheets Integration
Seamlessly connects with Google Sheets to allow users to turn their existing spreadsheet data into accessible APIs in real time. This integration makes it effortles
s to manage and update datasets without leaving the familiar Google Sheets interface.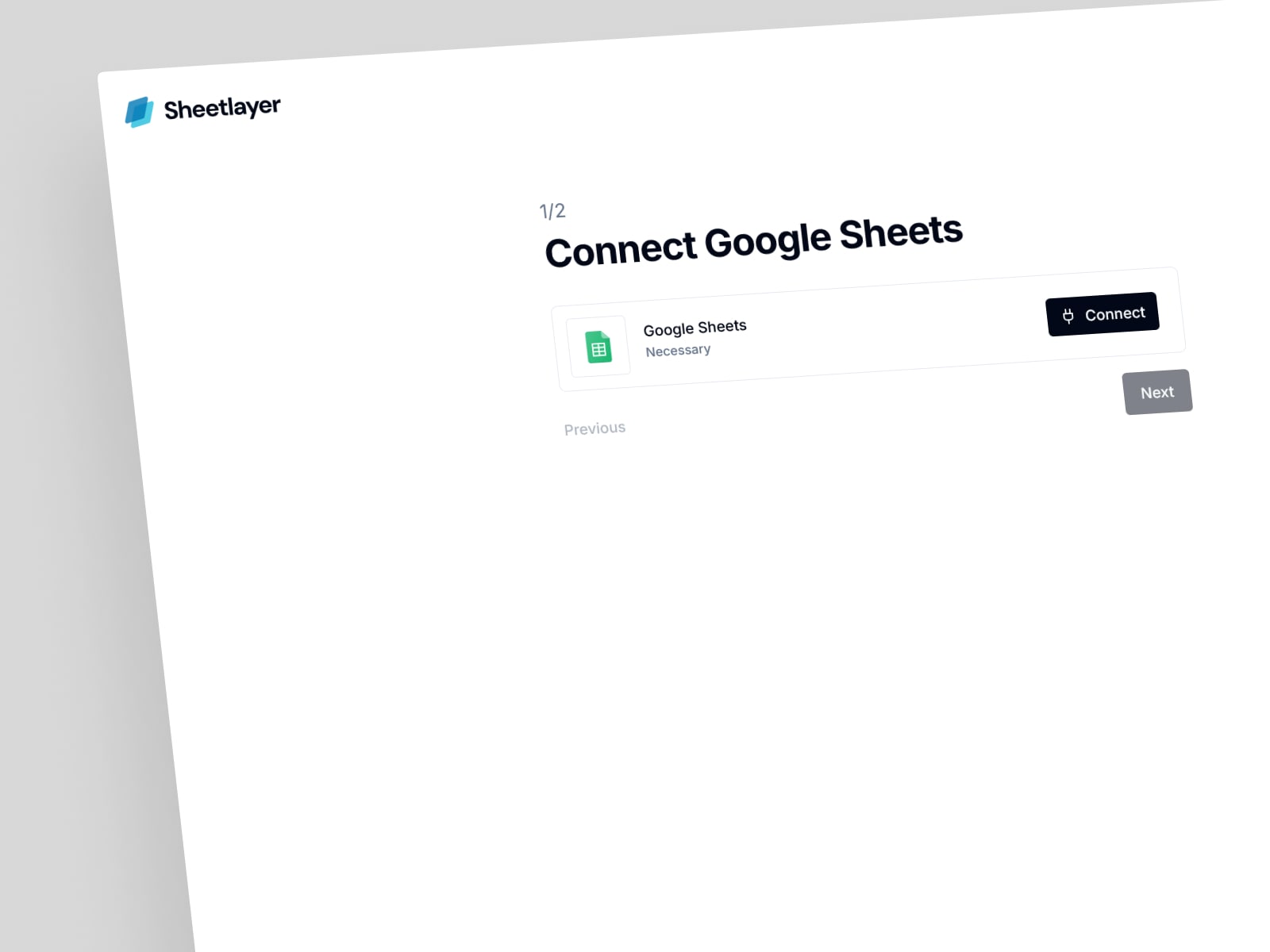
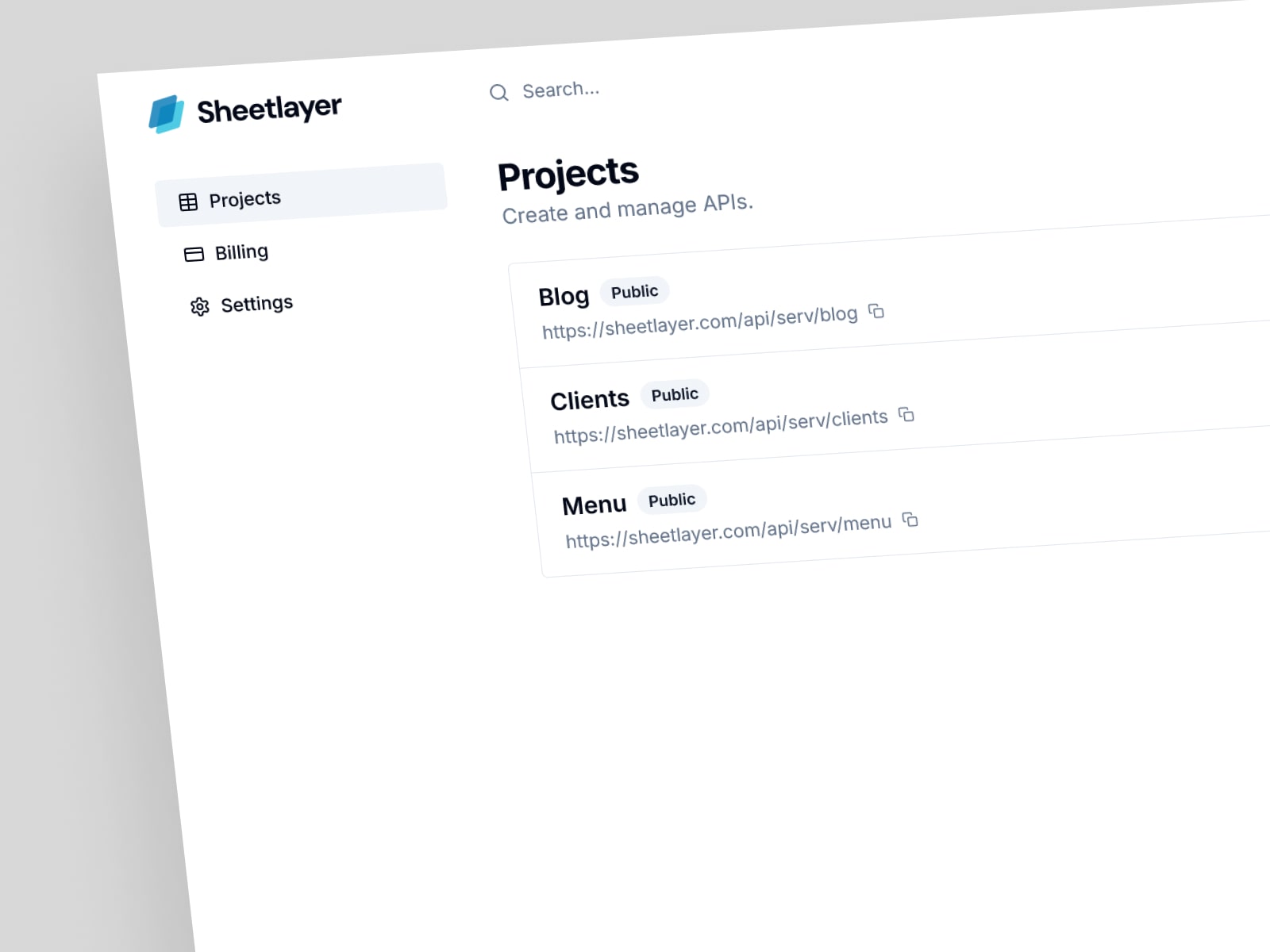
3. API Management
Provides tools to monitor, control, and secure all APIs created with SheetLayer. Users can view API usage statistics, set access controls, and make adjustments, enabling effective scaling and management of data-driven applications.
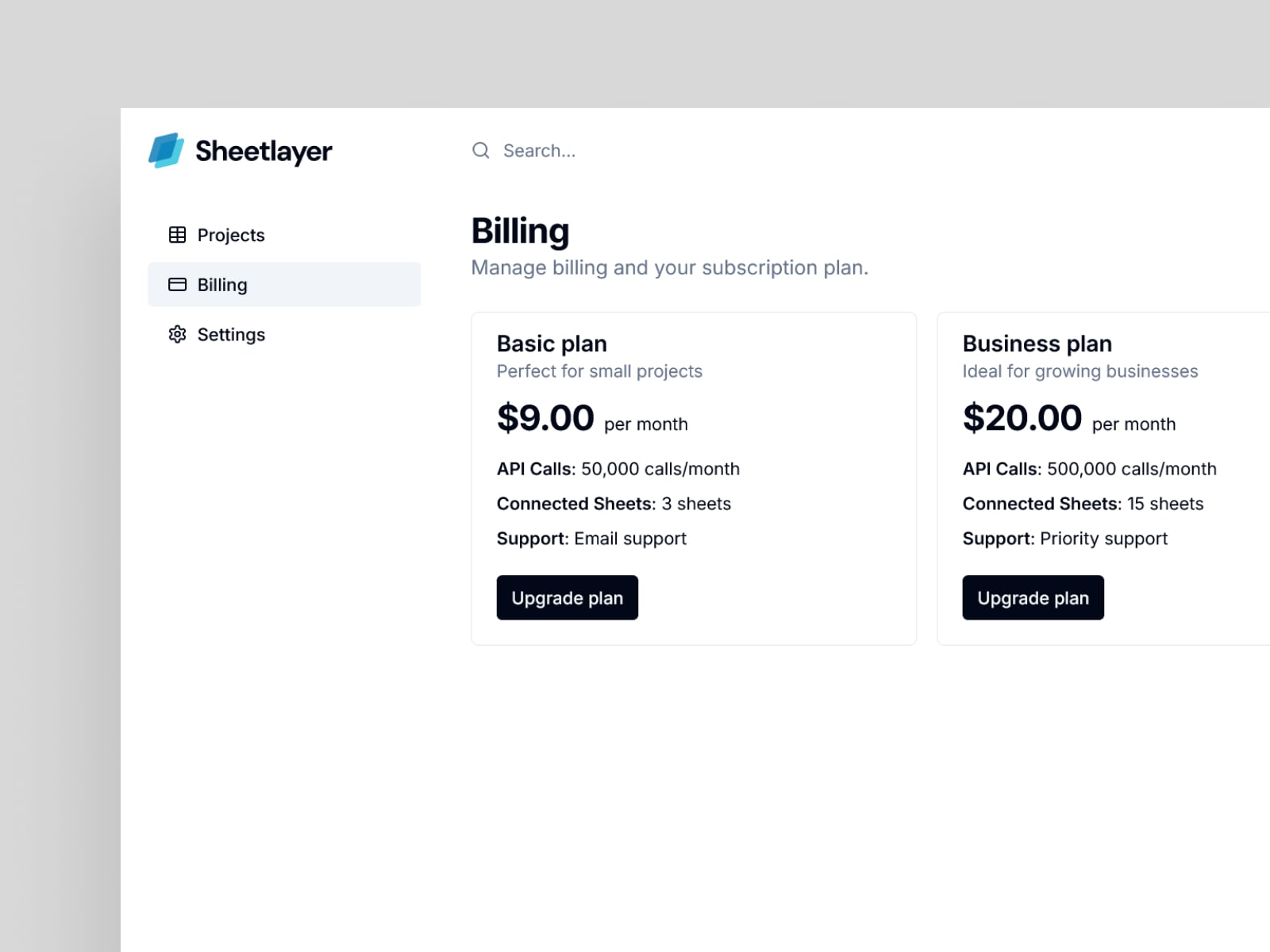
4. Billing Management
A user-friendly interface for managing subscription plans, viewing invoices, and tracking payment history. This feature helps users easily stay on top of their account, ensuring uninterrupted access to SheetLayer’s full suite of tools.
Database Schema
The SheetLayer schema supports a SaaS tool that integrates with Google Sheets to manage data and APIs. Its main components include:
-
User: Central to the application, this model manages user accounts with essential fields such as
email,picture, and timestamps for account lifecycle management. The relationship withSessionensures secure session handling and authentication. -
Api: Represents the APIs generated from user spreadsheets, including attributes like
title,spreadsheet, and timestamps. This model facilitates comprehensive management of API metadata within each user's workspace. -
Workspace: Organizes user projects by grouping related APIs under a unique identifier linked to a user. This structure fosters collaboration and efficient data management.
-
Subscription: Handles billing details and subscription plans, detailing
status, renewal dates, and pricing structures. This model allows users to seamlessly track their subscription status and billing information. -
Plan: Defines various subscription options available to users, outlining
productName,price, and usage-based billing preferences. This model supports flexible pricing strategies tailored to user requirements.
Technologies Used
-
Programming Languages:
- TypeScript: A superset of JavaScript that adds static types for improved error detection and code quality.
-
Frameworks and Libraries:
- Next.js: Used for server-side rendering and routing.
- React: For building interactive user interfaces.
- Tailwind CSS: For styling and maintaining design consistency.
-
Database and ORM:
- Prisma: Utilized for database access and migrations.
-
Email Services:
- Nodemailer: For sending emails easily.
-
State Management:
- Zustand: For managing application state.
-
Form Management:
- React Hook Form: For efficient form management and validation.
-
Payment Processing:
- LemonSqueezy: Integration for handling payments and subscriptions.
-
Utilities:
- Google APIs: For integrating with Google services, including authentication.
- Date-fns: For date manipulation.
-
Caching and Session Management:
- Redis: An in-memory data structure store, used for caching and session management.
-
Development Tools:
- ESLint: A tool for identifying and fixing problems in JavaScript code.
- Prettier: A code formatter to maintain a consistent code style.
Challenges Faced
Challenge
Security Against Brute Force Attacks: To prevent brute force attacks when generating login links and sending them via email, a Redis rate limiter was required to control the number of requests from a user. This helps ensure that no user can generate excessive login links within a short timeframe.
Solution
Implement a Redis-based rate limiter that restricts the number of login link requests a user can make within a specified time window. By utilizing Redis, we can efficiently track the number of requests and enforce limits to enhance security.
Code Snippet
Here’s the implementation of the Redis connection and rate limiter:
import { Redis } from "ioredis";
// Configuration Constants
const REDIS_URL = process.env.REDIS_URL || "redis://localhost:6379";
const RATE_LIMIT_WINDOW = 60 * 60; // 1 hour in seconds
const MAX_REQUESTS = 3; // Max requests per window
// Create Redis instance
const createRedisInstance = () => {
const { hostname, port, password } = new URL(REDIS_URL);
const redis = new Redis({
host: hostname,
port: parseInt(port),
password: password || undefined, // Use undefined if no password is set
tls: REDIS_URL.startsWith("rediss://") ? {} : undefined, // Enable TLS for secure connections
});
redis.on("error", (error) => {
console.error("Redis connection error:", error);
});
redis.on("connect", () => {
console.log("Successfully connected to Redis");
});
return redis;
};
const redis = createRedisInstance();
/**
* Rate limiter function
* @param {string} key - Unique key for the user (e.g., user ID or IP address)
* @returns {Promise<boolean>} - True if the request is allowed, false if it exceeds the limit
*/
export const rateLimiter = async (key) => {
try {
const currentCount = await redis.incr(key);
// Set expiration for the first request
if (currentCount === 1) {
await redis.expire(key, RATE_LIMIT_WINDOW);
}
// Check if the request exceeds the limit
if (currentCount > MAX_REQUESTS) {
console.warn(`Rate limit exceeded for key: ${key}`);
return false; // Exceeded limit
}
return true; // Request is allowed
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error in rateLimiter:", error);
return false; // Error occurred, deny request
}
};
export default redis;